A major challenge for living organisms is to maintain homeostasis in response to changes in external and internal environments. These include alterations in nutrient and water supplies, physical stress, temperature changes, physiological stress, infections and malignancies.
homeostasis 항상성
alteration 변화
malignancy 악성종양
Through billions of years of evolution, the forms of life and biological processes that cope with these challenges in the most successful way have been selected. One challenge that all organisms have to deal with is the elimination of microorganisms and of abnormal or damaged cellular material.
cope with ~에 대처하다
elimination 제거하다
abnormal 비정상적인
The ideal immune response would eliminate the potential threat and re-establish homeostasis without causing excessive damage to healthy cells and tissues. However, immune responses to infections are often disruptive and can cause marked tissue damage.
eliminate 없애다
re-establish ~을 재건하다
homeostasis 항상성
excessive 지나친, 과도한
disruptive 지장을 주는
Such responses are evolutionarily advantageous when the benefit of eliminating the challenge outweighs the risk of associated tissue damage and the requirement for regeneration. However, for potential challenges that occur frequently but rarely develop into serious homeostasis-altering threats, it is not desirable to mount systemic or potentially disruptive immune responses.
evolutionarily 진화론적으로
advantageous 이로운
outweigh ~보다 더 크다
regeneration 재생
desirable 바람직한
systemic 전체에 영향을 주는
In addition, vigorous immune responses are not desirable in organs and tissues that are particularly sensitive to immune-mediated damage, such as the brain. Therefore, the ideal immune response has checks and balances, which allow the organism to modulate the magnitude and duration of the response according to the nature of the threat caused by the challenge.
vigorous 격렬한
desirable 바람직한
particularly 특히
modulate 조절하다
magnitude 규모
duration 지속
The mammalian immune system, as we understand it today, is induced mainly by two types of receptor systems, the germline-encoded pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which initiate innate immune responses, and the antigen-specific receptors generated through gene rearrangement after antigen encounter, which initiate adaptive immune responses.
rearrangement 재배열
encounter 맞닥드리다
The immune responses induced by PRRs, such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs), interact with those induced by antigen-specific receptors; this interaction is notably represented by dendritic cells, which rely on PRR-driven cues to initiate dendritic cell maturation for the stimulation of lymphocytes through antigen-specific receptors.
notably 특히
cue 신호
stimulation 자극
initiate 개시되게하다
However, the research literature contains numerous reports of host defence activities that occur independently of both PRR-based immunity and antigen-specific receptors, and emerging evidence suggests that several of these mechanisms have non-redundant roles in host defence in humans.
literature 문학
independently of ~와 관계없이
non-redundant 중복되지 않는
Here we review the literature on this topic by focusing on constitutive immune mechanisms. On the basis of this analysis, and by integrating concepts previously reviewed, we propose that this constitutive layer of innate immunity exerts early host defence activities through specific molecular mechanisms and at the same time limits PRR activation as a specific feature.
constitutive 구성요소인
integrating 통합시키다
exert (영향력을) 가하다
Constitutive and inducible mechanisms
The innate immune system uses both constitutive and inducible mechanisms to eliminate infections and damaged self to maintain homeostasis.
eliminate 없애다

Although the constitutive mechanisms have the advantage of providing an immediate response to a danger signal, they lack the potential to amplify the response. In addition, constitutive mechanisms consume energy to remain operative, and there are hence limits to how many of these can be maintained in any one organism.
immediate 즉각적인
amplify 증폭시키다
consume 소모하다
hence 이런이유로
By contrast, inducible mechanisms such as those mediated through PRRs, as well as antigen-specific receptors, are activated only in response to stimuli and have the ability to amplify signals many times. Hence, inducible mechanisms can give rise to very strong and efficient immune responses, but can also lead to excess inflammation and immunopathology.
By contrast 대조적으로
mediate 중재하다
stimulus(stimuli) 자극제(의 복수형)
amplify 증폭시키다
excess 지나침
immunopathology 면역병리학
Given their amplification potential, inducible immune mechanisms require tight control and negative regulatory systems. The constitutive immune mechanisms can be divided into the chemical and physical barriers of the body, such as skin, saliva, stomach acid and urine flow, which are not the focus of this Review, and various molecularly defined mechanisms that control microbial infection and/or replication.
amplification 증폭
potential 잠재력
inducible 유도성의, 유발성의
tight 단단한
regulatory 규제력을 지닌
saliva 침, 타액
replication 응답
Although these mechanisms have been known for many years, they have generally been considered to have only minor roles in the immune system, and evidence has been lacking as to their specific, non-redundant functions in host defence.
Consequently, they have not received much attention in front-line immunology research. Here we discuss the constitutive innate immune responses in comparison with the better-described inducible innate responses triggered by PRRs. In addition, we present evidence suggesting that efficient action of constitutive innate immune mechanisms leads to both antimicrobial activity and mitigation of PRR-driven activities (Fig. 2).
comparison 비교
inducible 유치할 수 있는
mitigation 완화
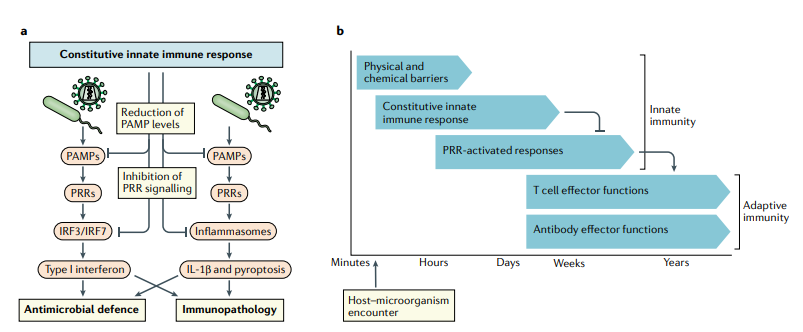
PRR-activated inducible innate immune responses.
PRRs detect pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), microorganism-associated molecular patterns, host derived danger-associated molecular patterns and molecular signatures associated with homeostasis altering molecular processes.
detect 감지하다
derived 파생된
These molecular patterns activate PRR signalling, which ultimately leads to the transcription of antimicrobial and proinflammatory genes. Downstream activities of PRR signalling include the production of type I interferon (interferon-α (IFNα) and IFNβ), IL-1β and tumour necrosis factor (TNF).
ultimately 궁극적으로
transcription 표기
proinflammatory 염증전
These cytokines, in turn, activate antimicrobial and proinflammatory activities, as well as the maturation of antigen-specific adaptive immune responses. PRR-based immune responses can be highly potent, and numerous inflammatory diseases are driven by excessive PRR signalling pathways.
However, the nature of PRR-based immunity is influenced by many factors, and it is worth mentioning that the gut microbiota and chronic viral infections can induce PRR-based, host-beneficial responses that tend towards tolerance rather than inflammation.
gut microbiota 장내 미생물군
chronic viral 만성 바이러스
tolerance 내성
Nevertheless, given the potency of PRR-based immunity, full activation of PRR-driven immune responses each time a microorganism is encountered may not be beneficial for an organism in the longer term. Moreover, it is essential to control the activation and duration of PRR signalling-induced activities.
potency 힘
activation 활성화
each time 언제나
encounter 맞딱드리다
duration 지속
This is achieved through multiple mechanisms, including two-step procedures for full PRR activation, the requirement for a threshold PAMP concentration to achieve PRR activation, amplification loops from initial low responses and numerous negative-feedback mechanisms.
procedures 절차
threshold concentration 최저 유효 농도
amplification 증폭
One way in which the activation of PRR signalling in response to very low levels of PAMPs is avoided at the molecular level is through supramolecular organizing centres. These are higher-order signalling complexes at specific subcellular locations that rely on amplification mechanisms to achieve full activation, thus preventing signalling by subthreshold levels of PAMPs but amplifying signalling by superthreshold levels of PAMPs.
activation 활성화
supramolecular organizing centres(SMOCs)
higher-order 고차원
subthreshold (자극이) 반응을 일으키기에는 불충분한
The double-edged sword-like nature of PRR-induced immune responses in terms of their roles in both protection and disease is also supported by evolutionary evidence. This includes the recurring loss of 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthase 1 (OAS1) in primates. OAS1 is an interferon-inducible protein that is associated with both antiviral and pathological activities.
double-edged sword (긍정과 부정의) 양면성을 지닌 상황[결정]
Constitutive innate immune mechanisms.
Constitutive innate immune mechanisms respond to microbial activities, cellular stress and metabolic alterations by inducing antimicrobial effector functions. As there is most evidence for constitutive innate immune mechanisms that exert antiviral and antibacterial activities, these are the focus of this Review.
metabolic 신진대사의
alterations 변화
constitutive 구성요소인
exert 가하다
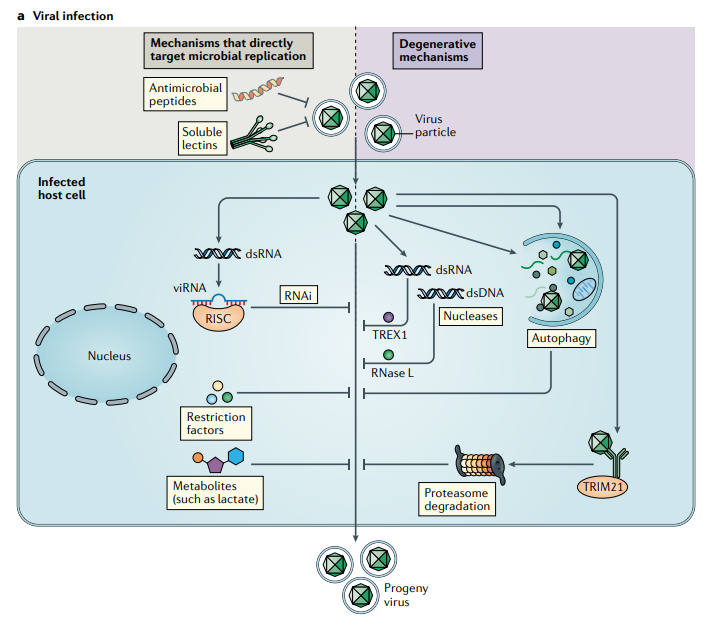
a | Constitutive innate immune mechanisms and viral infection. The accumulation of specific viral molecular structures (such as double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) or capsids) and cellular stress responses (such as autophagy) activate constitutive–latent mechanisms with direct antiviral activity, independently of pattern recognition receptors.
accumulation 늘어나다
constitutive 구성요소인
latent 잠재하는
independently of ~와 관계없이
Some of the antiviral effector functions target microbial replication by blocking specific steps in the replication cycles of viruses; these effectors include soluble lectins, antimicrobial peptides, restriction factors, RNA interference (RNAi) and metabolites. Other antiviral effectors of the constitutive response function through the degradation of virus particles; these include nucleases such as TREX1, which degrades viral DNA in the cytoplasm, and RNase L, which degrades viral RNA, as well as autophagy and proteasomal degradation. Viruses can be targeted for proteasomal degradation by the ubiquitin E3 ligase TRIM21, which binds to antibody-attached viral capsids.
effector 반응기
replication 복제
metabolites 대사물질
constitutive 구성요소인
degradation 분해
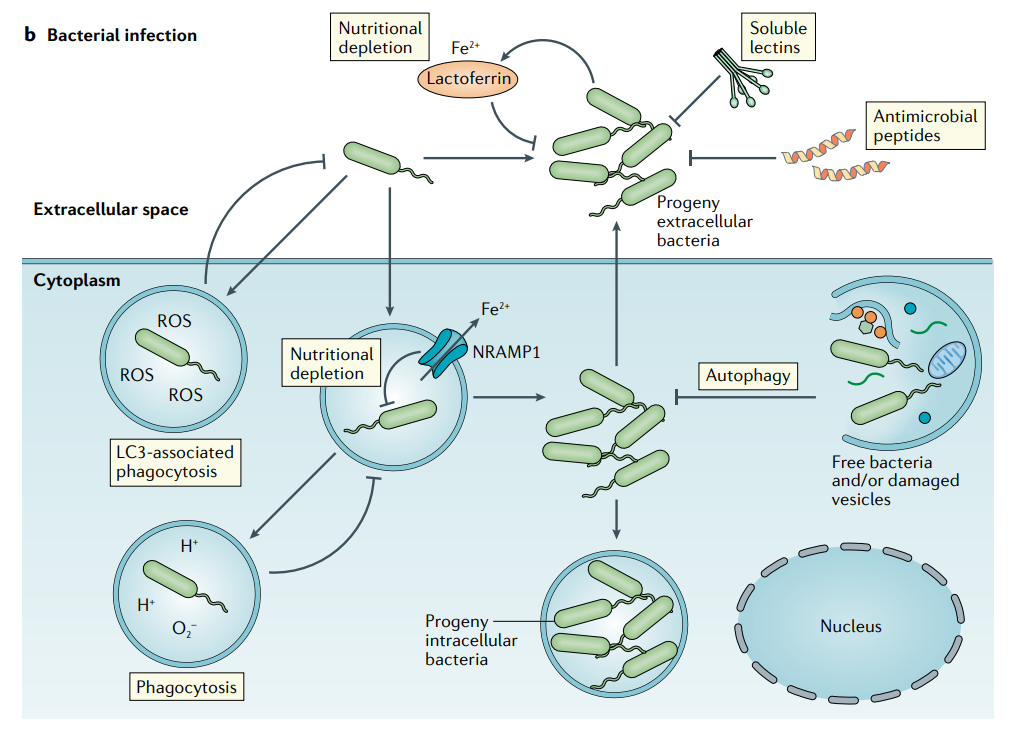
b | Constitutive innate immune mechanisms and bacterial infection. The presence of bacteria changes the local microenvironment, for example through the accumulation of hydrophobic and charged bacterial surfaces or alteration of cellular metabolism. This activates antibacterial activities independently of pattern recognition receptors, including inactivation by soluble lectins and antimicrobial peptides, nutritional depletion by natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 1 (NRAMP1) and lactoferrin, and bacterial degradation by phagocytosis and basal autophagy. dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; ROS, reactive oxygen species; viRNA, virus-derived small interfering RNA.
A large range of constitutive mechanisms of innate immunity have been identified, including restriction factors, antimicrobial peptides, basal autophagy and proteasomal degradation.
constitutive 구성요소인
identified 식별된
restriction 제한
degradation 분해
Here we divide these mechanisms into two classes: those that target specific steps in microbial replication cycles, such as restriction factors, and those that lead to degenerative processes, such as autophagy.
replication cycles 복제주기
The constitutive mechanisms that target specific steps in microbial replication function by blocking molecularly defined events that are essential for the replication of specific microorganisms but are dispensable for cellular fitness.
molecularly 분자에 의하여
dispensable 불필요한
fitness (신체적인) 건강
By contrast, those mechanisms that operate through degenerative programmes target microbial or altered host molecules for recycling or degradation. The modes of action of representative examples from each of these mechanistic classes are described in the following sections.
By contrast 대조적으로
degenerative 퇴행성의
degradation 분해
mechanistic 기계론적인
Given the ability of constitutive immune mechanisms to exert antimicrobial activity, one consequence of their successful action is decreased levels of PAMPs (Fig. 2a). This, in turn, limits PRR activation and the downstream inflammatory response (Fig. 2b).
exert 가하다
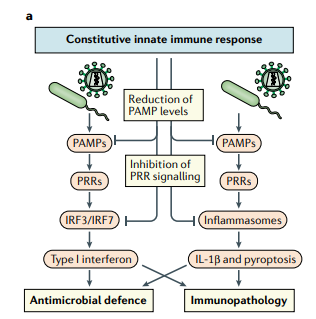
Thus, constitutive immune mechanisms equip cells and tissues with a layer of defence that can fight infections immediately and hence potentially limit the requirement for inducible immune responses, such as type I interferon, IL-1β and other proinflammatory cytokines.
equip 준비를 갖춰주다
potentially 잠재력
inducible 유치할 수 있는
proinflammatory 염증전