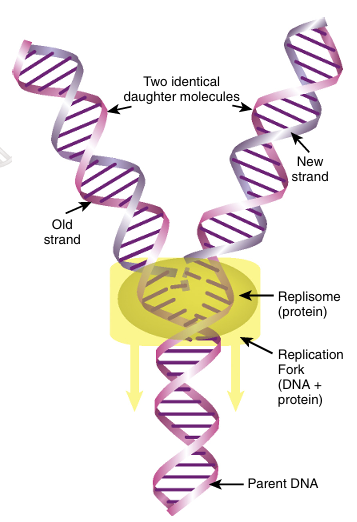
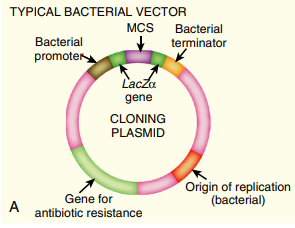
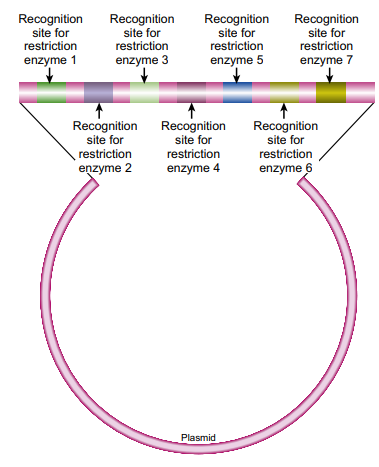
INTRODUCTIONReplication copies the entire set of genomic DNA so that the cell can divide in two. During replication, the entire genome must be uncoiled and copied exactly. This elegant process occurs extremely fast in E. coli, where DNA polymerase copies about 1000 nucleotides per second. Although the process is slower in eukaryotes, DNA polymerase still copies 50 nucleotides per second. Many bi..