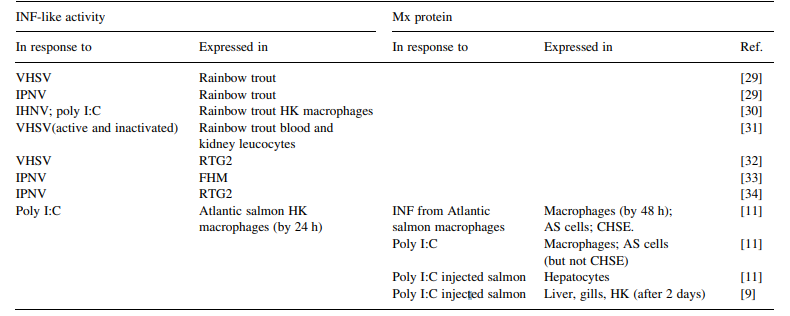
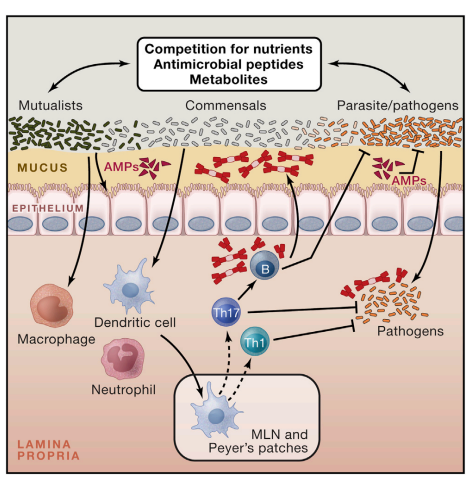
1. INTRODUCTIONThe canonical Th1 cytokine, interferon-γ (IFN-γ), is critical for innate and adaptive immunity against viral and intracellular bacterial infections. In humans, genetic deficiencies in the interleukin (IL)-12/IL-23/IFN-γ pathways that result in decreased IFN-γ induction or signaling are associated with strikingly increased susceptibility to mycobacterial infections (Filipe-Santos e..