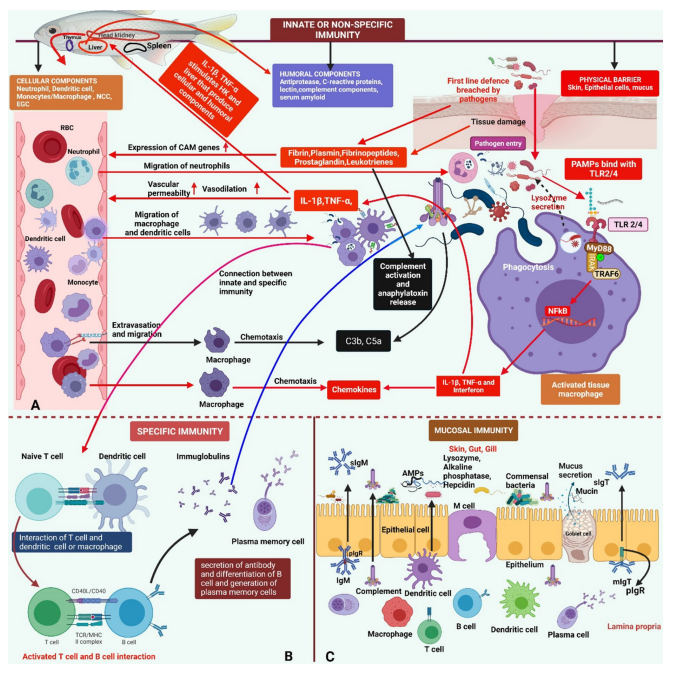
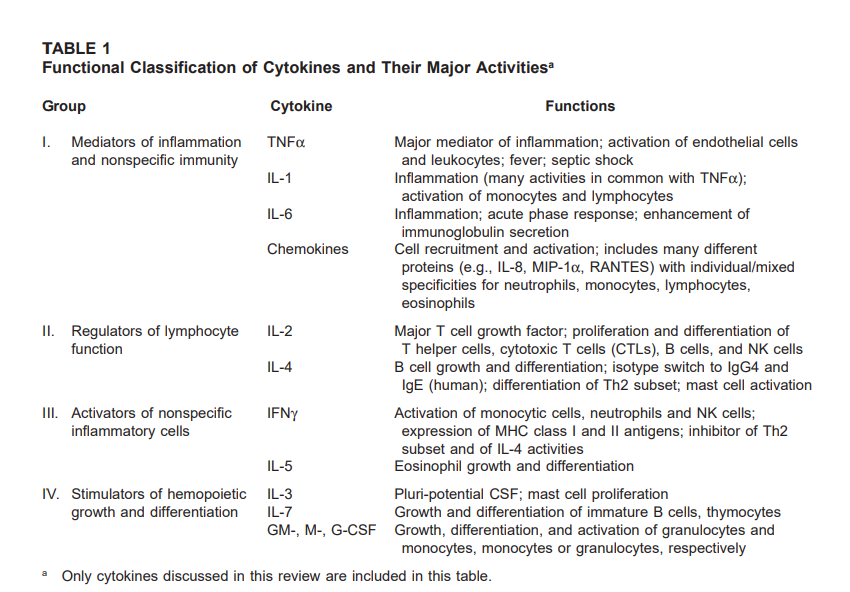
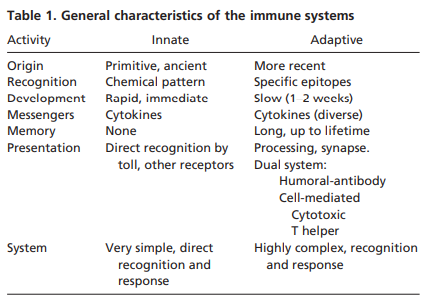
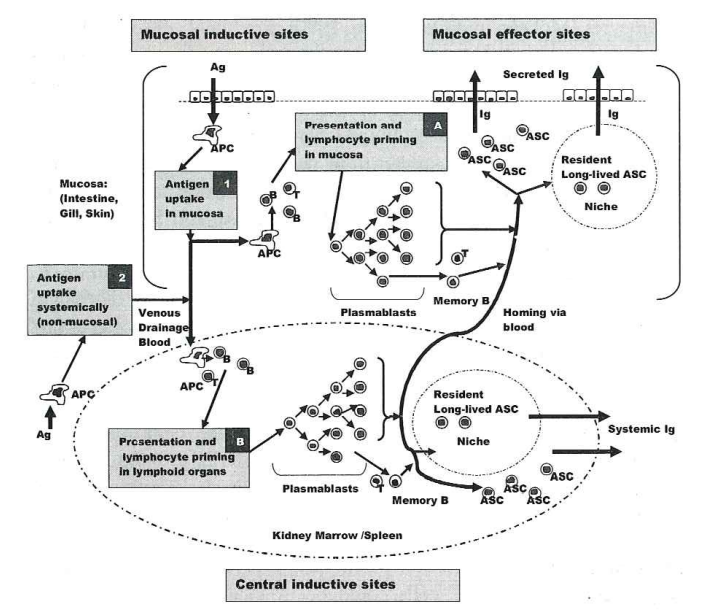
1. IntroductionMost infections start at or affect the mucosal epithelia of animals. Mucosal surfaces face many antigens while living in harmony with commensal microorganisms, known conjunctionally as microbiota. Over the last few years, the literature has been filled with many studies on how the microbiota shapes the host and its immune system [1e3]. Commensal colonization brings many physiolog..