4. Cellular Immune Components
The immune cell populations present in fish are not very different from those found in mammals. Immune cells in teleosts include natural killer cells, non-specific cytotoxic cells, macrophages, granular leucocytes, thrombocytes, monocytes, dendritic cells, lymphocytes, mast cells, and eosinophilic granule cells. In addition, fish also possess rodlet cells and melanomacrophage centers.
4.1. Natural Killer (NK) Cells
In teleost fish, there are two different types of NK cell homologs: non-specific cytotoxic cells (NCCs) and NK-like cells [63]. In contrast to NK cells, which have a large and granular morphology, NCCs are tiny, agranular cells that resemble catfish monocytes. [64]. NCCs in seabream are highly variable in morphology [65].
homolog 동족체, 상동하는 것
In contrast to ~와는 대조적으로
granular morphology 과립모양 형태
agranular cells 무과립세포
variable 변동이 심한
morphology 형태학
The discovery of NK-like cells in teleosts suggests that NCCs are not the same as NK cells in fish. Accordingly, NK-like cells destroy allogeneic and virus-infected cells, according to a few investigations conducted on rainbow trout and catfish [63].
allogeneic 동종이계
종은 같으나 다른 개체의 세포/조직
investigation 수사, 조사
From teleost NK-like cells, the gene that acts as a cell marker, NK cell enhancement factor (NKEF), has been discovered. After viral and bacterial infection, NKEF gene expression is elevated in tissues such as the skin, gills, and other organs. [66]. Interestingly, a recombinant NKEF protein enhances the cytotoxicity of NCC from the kidney in Nile tilapia [66].
elevated 높은
Interestingly 흥미롭게도
recombinant 재조합형
cytotoxicity 세포독성
The NCCs were the first recognized and are the most thoroughly investigated killer cell population in teleosts. The NCCs serve functions like those of the higher vertebrates, acting on various target cells, including virus-infected cells, tumor cells, and protozoan parasites. NCCs may also be involved in antibacterial immunity by triggering the production and secretion of cytokines [67].
investigated 조사된
serve 제공하다
protozoan parasite 원생 기생충
secretion 분비
The NCCs of tilapia and catfish express components of the granule exocytosis pathway of cell-mediated cytotoxicity (CMC) analogous to cytotoxic lymphocytes of mammals [68].
analogous 유사한
granule exocytosis pathway 과립세포외 배출경로
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte and natural killer cell-initiated cell death is one of the primary mechanisms used by higher organisms to eliminate viruses and transformed cells. In this context, target cell death is rapid and efficient and initiated via two main pathways, involving either the ligation of death receptors or through the granule-exocytosis pathway.
cell-mediated cytotoxicity 세포 매개 독성
Non-specific CMC reactions in mammals are mainly performed by NK cells. Non-specific cytotoxic cells (NCCs) and NK-like cells, two classes of NK cell homologues, are responsible for non-specific CMC mechanisms in fish. Fish NK-like cells have been isolated from blood leukocytes and have been shown to kill virus infected, allogeneic, and xenogeneic target cells on their own [34].
xenogeneic 이종(異種)의
NCCs, on the other hand, tend to target a variety of cells, including some protozoa and tumor cells, and are particularly active in the spleen and head kidney. NCCs are capable of spontaneously killing the affected cells through necrotic and apoptotic mechanisms [27].
capable ~을 할 수 있는
spontaneously 자연스럽게
necrotic : producing death of a usually localized area of living tissue; marked by necrosis(생체 내 조직·세포의) 괴사
apoptotic 세포사멸제
These cells show variable morphological features, varying from tiny agranular monocyte like cells in catfish to a mixture of acidophilic granulocytes, monocyte-macrophages, and lymphocytes in seabream [69].
variable 변동이 심한
morphological features 형태적 특징
agranular monocyte 무과립 단핵구
Moreover, a population of circulating lymphocytes that resemble mammalian natural killer (NK) cells in terms of morphology and functionality has also been reported [70].
circulating 순환하는
mammalian 포유류의
in terms of ~면에서는
morphology 형태학
functionality 기능성
Additionally, NCCs express the NCC receptor protein 1 (NCCRP-1) on their cell surface and present a vimentin-like surface molecule [71]. It has been shown that catfish NCCs recognize and kill various human cell lines [64]. Further research reported that granulysin, perforin, and serglycin, gene-encoding molecules with lytic capacity, are expressed by NCCs [72]. Finally, the fish possess different NCC subsets in several of their immune compartments [73].
subset 부분집합
4.2. Macrophages
Macrophages have a pivotal role in specific immune responses because of their function in lymphocyte activation and phagocytosis. Macrophages possess specific receptors capable of recognizing β-glucan, so that the immunostimulants augment leukocytes’ respiratory burst, which produces reactive oxygen species with bactericidal activity [74].
pivotal 중심이 되는
immunostimulants 면역자극
augment 늘리다
respiratory burst 호흡폭팔
bactericidal activity 향균력
Respiratory burst (RB) is a rapid increase in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) during the phagocytosis of microbes.
호흡폭발(Respiratory burst)은 주변 세포들로부터 활성 산소종(reactive oxygen species)이 급격하게 분출되는 현상을 말한다. 주로 대식세포 등의 식세포작용을 통해 염증 반응에 관여할 때 생성된 과산화수소 및 산화질소종으로 인해 발발한다.
β-glucan
Another bactericidal mechanism is represented by the production of nitric oxide (NO), which is catalyzed by an NO synthase. Using enzyme histochemical techniques, Schoor and Plumb [75] demonstrated inducible NO production from the head kidney of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) infected with Edwardsiella ictaluri.
represent 대표하다
nitric oxide 산화질소
catalyze 촉진시키다
synthase 신타아제 ((역방향으로 리아제 반응을 하는 효소), NO synthase 일산화질소합성효소
histochemical 조직화학의
In addition, Stafford et al. [76] distinguished the molecules found in crude leukocyte supernatants that stimulate NO production in macrophages of goldfish, indicating that transferrin is an essential mediator for the activation of both fish granulocytes and macrophages.
distinguish 구별하다
crude 대강의
stimulate 자극하다
indicate 나타내다
mediator 중재인
granulocytes 과립성백혈구
In fish, neutrophils and macrophages play an essential role in controlling the spread of infectious agents and are accountable for the destruction of phagocytosed pathogens [77].
neutrophils 호중구
infectious 전염이 되는
controlling 통제
accountable 책임이 있는
destruction 파괴
phagocytosed 포식작용
Macrophages act as antigen-presenting cells in the distal intestine, enabling antigens to interact with the adaptive immune system for identification. Other granulocytes can also be identified in the intestinal segments for innate clearance, in addition to the resident macrophages [78].
enabe 가능하게 하다
interact 소통하다
identification 인지
intestinal 장의, 장에 기생하는
segments 부분
clearance 없애기, 정리
resident 거주자
The lamina propria and epithelial linings of the intestine contain these innate populations, allowing a close vicinity to the digested pathogens. Macrophages express several receptors on their cell surface, including TLRs, PRRs, and CLRs, in addition to complement and scavenger receptors.
lamina propria 기저막
lining 내벽
vicinity 부근
digest 소화하다
scavenger 청소부
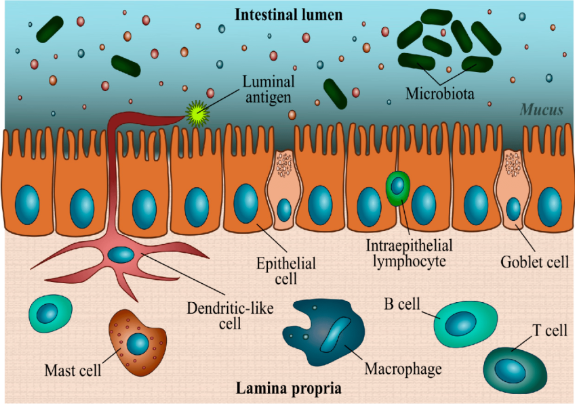
Macrophages are also an essential source of chemokines and cytokines, linking innate and adaptive immunity, which mediates an efficient immune response [79]. Moreover, macrophages are important for antigen presentation to T cells [80].
chemokine 케모카인
백혈구뿐만 아니라 다른 방향성 운동을 유도하는 세포에서 분비하는 작은 사이토카인 또는 신호 전달 단백질 계열
mediate 영향을 주다
Circulating monocytes are typically CD14+, and express chemokine receptors, TLRs, adhesion molecules, and surface molecules that are involved in the pathogen-associated molecular pattern recognition at sites of inflammation and/or infection [81].
Circulating 순환하는
typically 보통
adhesion 접착력
inflammation 염증
infection 감염
4.3. Neutrophils
In the blood, peritoneal cavity, and lymphoid organs, neutrophils are polymorphonuclear cells that have the ability to phagocytose / cells or foreign particles and manufacture superoxide anions, a bactericidal component [82].
peritoneal cavity 복강
lymphoid organs 림프기관
neutrophils 호중구
polymorphonuclear 다형핵(백혈구)구
manufacture 제조하다
superoxide 초과산화물 (O2-를 포함하는 화합물)
bactericidal 살균의
Neutrophils play an essential role in the inflammatory immune response against various viral, bacterial, fungal, and protozoan pathogens [79]. Neutrophils are the first granulocytes to be detected at the injury site, followed by macrophages, both of which are directed by chemotactic factors produced by wounded tissue.
Neutrophils 호중구
inflammatory 염증을 일으키는
viral 바이러스성의
granulocytes 과립구
injury 상처
directed 유도된
wounded 부상을 입은
chemotactic factors
Definition. Chemotactic factors are substances that stimulate cellular locomotion/migration
At the site of injury, neutrophils use antimicrobial peptides, proteolytic enzymes, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) to phagocytose microorganisms and destroy them [83].
proteolytic enzymes 단백질 가수분해 효소
Additionally, fish neutrophils have the ability to release extracellular fibers known as neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) that include DNA, histones, and proteins that can bind, kill, and inactivate viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites [84].
neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) 호중구 세포외 트랩
Furthermore, the granular leukocyte-derived myeloperoxidase enzyme can interact with hydrogen peroxide to create hypochlorite, which in turn can be used to produce cloramins, oxidative substances that can attack microorganism membranes [85].
myeloperoxidase 골수세포형과산화효소
interact 상호작용하다
hydrogen peroxide 과산화수소
hypochlorite 차아염소산염
oxidative 산화의
4.4. Eosinophils, Basophils, Thrombocytes, and Monocytes
Eosinophils are widely distributed cells in connective tissue, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract, bloodstream, ovaries, and gills, and offer degranulation when parasite infections are present [86].
Eosinophils 호산구
distributed 분포된
gastrointestinal tract 위장관
bloodstream 혈류
ovaries 난소
degranulation 탈과립
탈과립(degranulation)은 일부 세포 내부에서 발견되는 과립이라고 하는 분비 소포로부터 항균성 세포독성 또는 기타 분자를 방출하는 세포 과정이다
Basophils are large polymorphonuclear granular leucocytes that are rarely observed in teleost species [87]. Their cytoplasmic granules have an inflammatory mediator, histamine. These cells are involved in allergy and anaphylaxis [88].
Basophils 호염기구
polymorphonuclear 다형핵
granular leucocytes 과립구
cytoplasmic granules 세포질과립
inflammatory mediator 염증매개체
anaphylaxis 과민증
histamine
히스타민은 외부자극에 대하여 신체가 빠른 방어 행위를 하기 위하여 분비하는 유기 물질 중의 하나이다. 즉, 상처가 난 곳이 붉게 부어오르며 통증을 느끼게되는 염증반응이 일어나게 하는 물질이다.
Thrombocytes are oval-shaped, nucleated, and agranular cells.
Thrombocyte 혈소판
oval-shaped 타원형
agranular cells 무과립세포
과립에는 세균과 다른 외부 세포를 죽여서 삼키는 효소와 기타 물질이 들어 있습니다.
They possess both a coagulation function and phagocytic ability. They show acid phosphatase activity that causes cells to gather at the inflammatory site [89].
coagulation 응고
acid phosphatase 산성인산분해효소
포스파타아제 (생체 조직에 있는 유기산과 에스테르, 폴리인산을 가수 분해하는 효소)
The monocytes show phagocytosis and non-specific cytotoxic activities. These cells are thought to be transient blood cells because they migrate to the connective tissue during the inflammatory phase and change into macrophages [89].
monocytes 단핵구
단핵구(單核球, 영어: monocyte)는 혈액 내에 존재하는 식세포의 일종으로 대식세포나 수지상 세포로 분화할 수 있다.
transient 일시적인
migrate 이동하다
Professional phagocytes that can be deployed to the site of inflammation include monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and dendritic cells [90].
deploy 배치하다
'Main Components of Fish Immunity' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Main Components of Fish Immunity - 6. Immunoglobulins (0) | 2024.11.17 |
|---|---|
| Main Components of Fish Immunity - 5. Mucosal Barriers (0) | 2024.10.06 |
| teleost fish 계통분류 (0) | 2024.10.06 |
| Main Components of Fish Immunity - 4.5. - 4.9. Cellular Immune Components (0) | 2024.10.05 |
| Main Components of Fish Immunity - Innate Immune System & Antigen Processing and Presentation (0) | 2024.10.03 |