1. THEORY
Molecular cloning is an essential technique to create DNA-based experimental tools for expression in bacterial or mammalian cells.
Examples of such DNA constructs include a promoter element fused to a reporter gene or a cDNA sequence under the control of a ubiquitous promoter.
Molecular cloning entails the preparation of the vector and insert DNAs, ligation of the insert into the vector, transformation of competent E. coli, and identification of positive clones (Fig. 7.1).
Traditionally, molecular cloning is defined as the isolation and amplification of a specific DNA fragment. Most of these fragments are created either by digesting an existing piece of DNA with restriction enzymes or by targeting it via PCR. Short inserts of 100 bp can also be commercially synthesized as complementary single-stranded oligos, which are subsequently annealed to form a double-stranded fragment.
amplification 증폭
After successful isolation, the DNA of interest is ligated into a vector plasmid, a double-stranded circular piece of DNA that can be propagated in E. coli. Vectors used in the laboratory represent a smaller version of naturally occurring plasmids that include several basic features: a replication origin, a drug-resistance gene, and unique restriction sites to facilitate the insertion of DNA fragments.
Often, several different restriction sites are clustered together in so-called ‘polylinker regions’ or ‘multiple cloning sites,’ making it easier to choose convenient and unique restriction enzyme combinations for a variety of inserts. The choice of restriction enzymes is critical when designing a cloning strategy.
A multiple cloning site (MCS), also called a polylinker
While some sever the double-stranded DNA in one place, creating ‘blunt’ ends, others leave an overhang of a few bases at the cut site. These complementary ‘sticky’ ends find one another easily, increasing the efficiency of the ligation reaction and thus the chances for a successful cloning event. Thoughtful combination of restriction enzymes can also help to control the directionality of the insert, which is critical to many applications.

2. EQUIPMENT
Microcentrifuge
Shaking incubator (37 C)
Incubator (37 C)
Heating block or water bath (42 C)
Heating block (65 C) (optional)
Bunsen burner
agarose gel electrophoresis equipment
1.5-ml microcentrifuge tubes
15-ml polypropylene tubes
Micropipettors Micropipettor tips (autoclaved)
3. MATERIALS
Vector DNA (receiving vector, insert vector or insert PCR product)
Insert DNA
Restriction enzymes
10 * Restriction enzyme buffers
10 * BSA
Agarose
Tris base
EDTA
Glacial acetic acid
Ficoll
Bromophenol blue
Xylene cyanol
Ethidium bromide
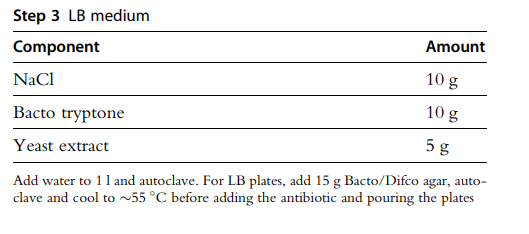
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Bacto tryptone
Yeast extract
Bacto/Difco agar
10 * DNA T4 ligase buffer
T4 DNA ligase
Chemically competent E. coli
Antibiotic (e.g., ampicillin, kanamycin)
DNA Gel purification kit
PCR purification kit
optional: 10 * Restriction enzyme buffer #2 (NEB2), 2.5 mM dNTPs, Klenow fragment, 0.5 M EDTA
3.1. Solutions & Buffers

'Molecular Cloning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Molecular Cloning - 4. PROTOCOL(보류) (0) | 2024.11.08 |
|---|