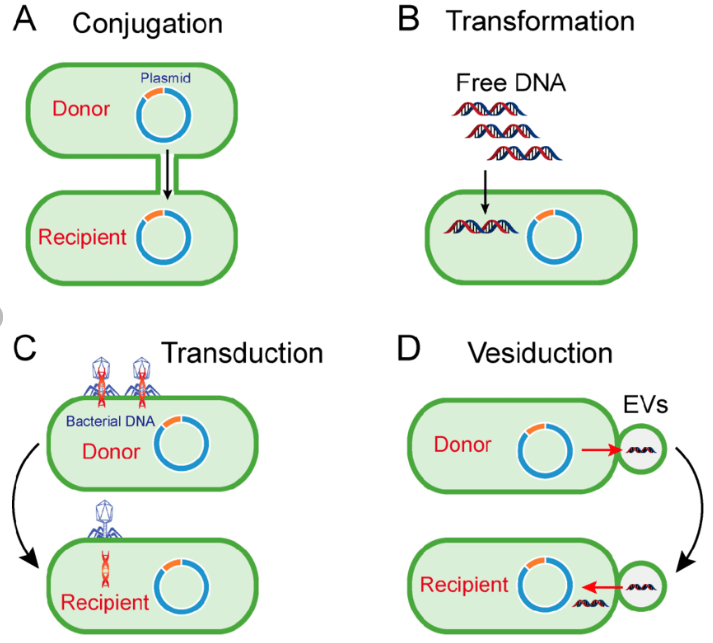
Plasmids are extrachromosomal DNA elements with characteristic copy numbers within the host. These replicons have been found in species from the three representatives of the living world, namely, the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya (318). Plasmids may constitute a substantial amount of the total genetic content of an organism, representing more than 25% of the genetic material of the cell..