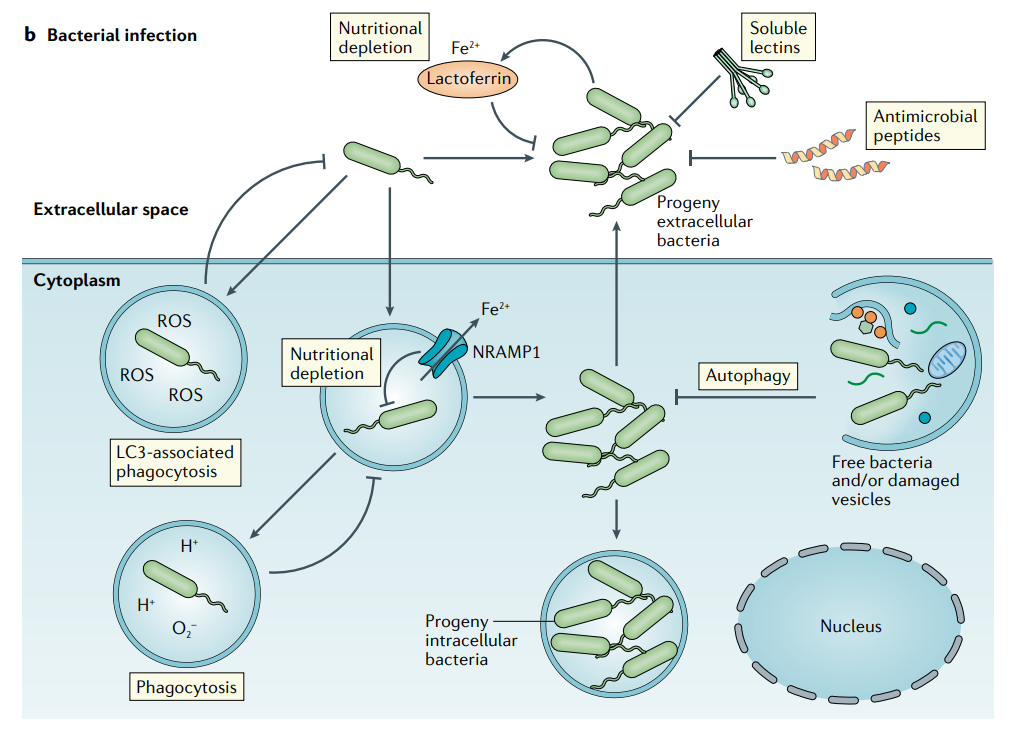
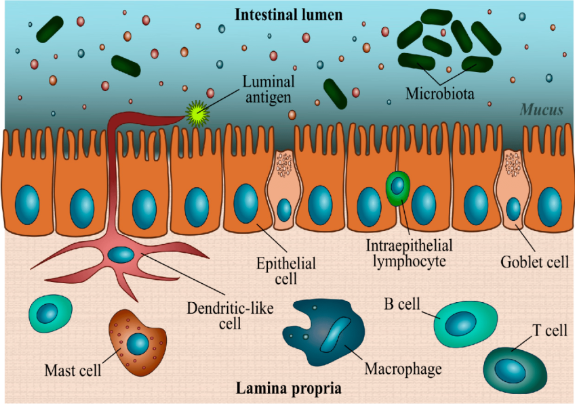
The use of the viruses of bacteria, bacteriophages (phages), as therapeutic agents to treat bacterial infections began 20 years before the first clinical use of an antibiotic drug, but the introduction of broad-spectrum antibiotics in the 1940s rapidly eclipsed and displaced the development of phage therapeutics in much of the world. therapeutic agents 약제 drug 약물broad-spectrum 폭넓은 효능을 지닌therapeu..