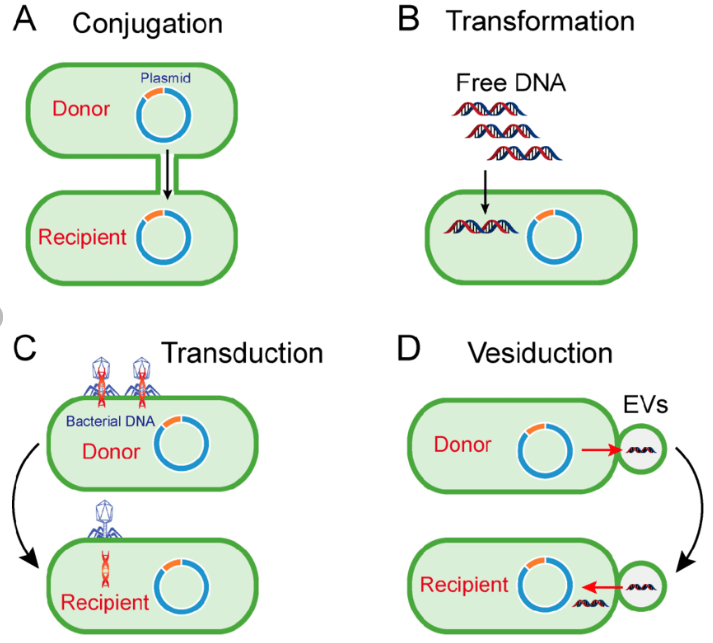
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA was first achieved in 1973 Herbert Boyer, of the University of California at San Francisco, and Sta..