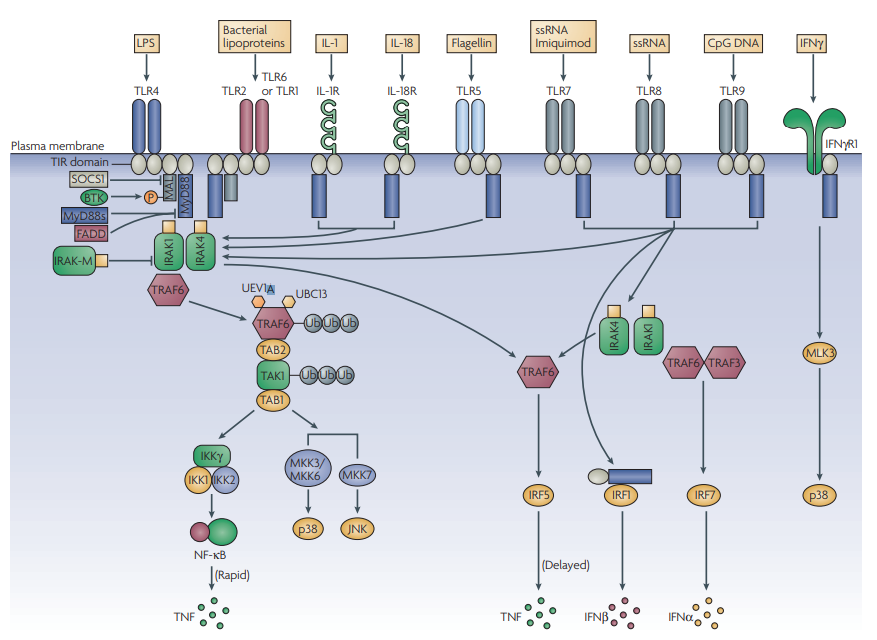
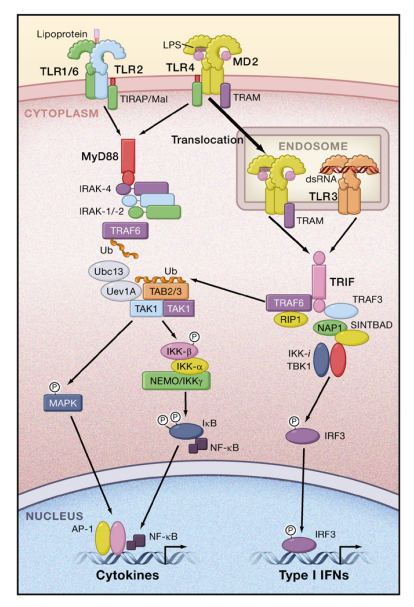
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are of interest to immunologists because of their front-line role in the initiation of innate immunity against invading pathogens1 . The signalling pathways activated by different TLRs have therefore been the focus of much research. TLR signalling involves a family of five adaptor proteins, which couple to downstream protein kinases that ultimately lead to the activati..