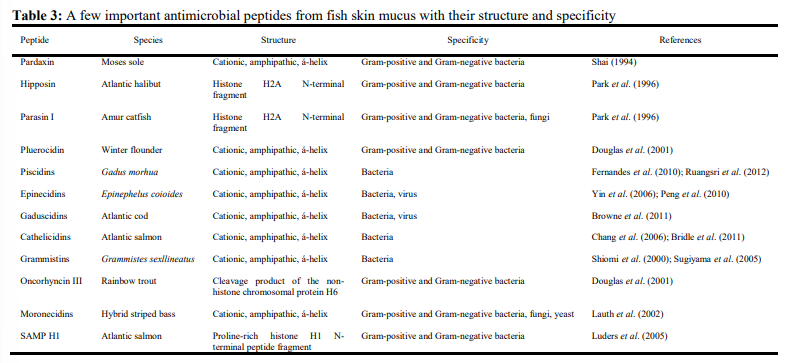
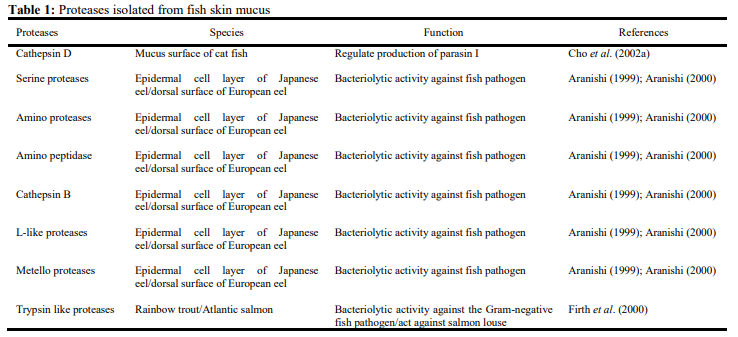
Other innate immunity components in fish mucusThere are also a few important components of fish epidermal mucus which play an important role in innate immunity of fishes such as C-reactive proteins (CRPs), transferrin, ALP, complement proteins, etc. CRPs belong to a family of multifunctional proteins (pentraxins) and are capable of binding various ligands in a Ca2+ dependent binding affinity. Th..