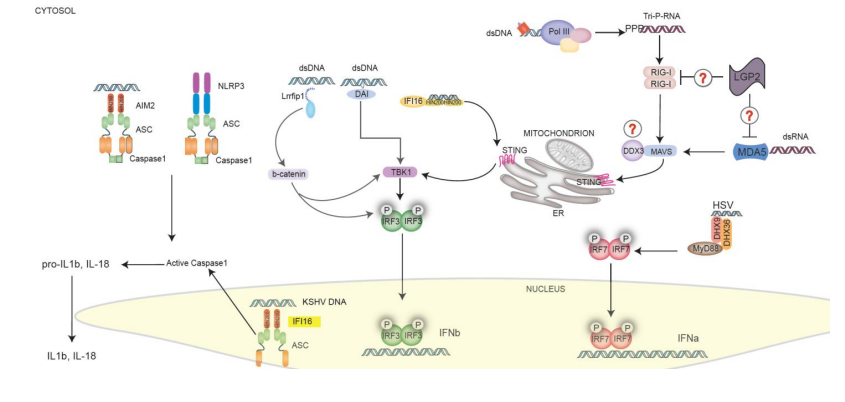
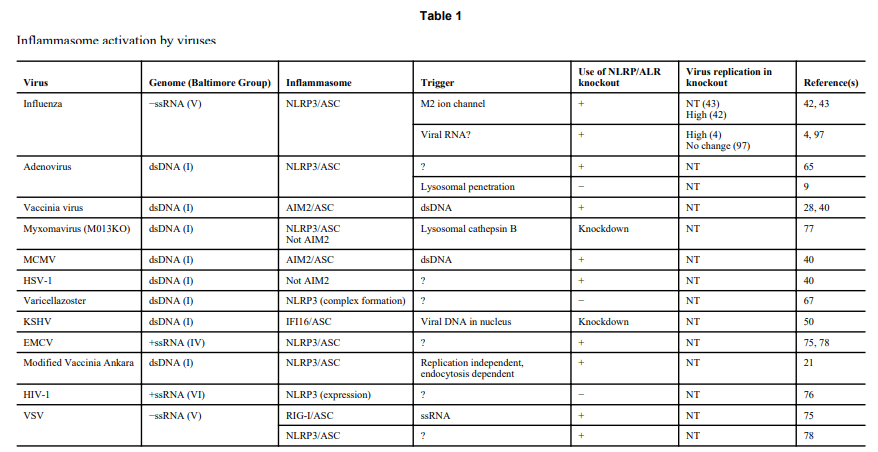
3. Intracellular Nucleic Acid SensorsAs discussed above, the TLRs play an important role in sensing viral PAMPS that are present within the extracellular compartment, as well as in endosomes. In certain contexts, TLRs can receive viral nucleic acids generated from viruses that replicate in the cytoplasm, via an autophagy mechanism. A role for intracellular sensors in the clearance of viruses tha..