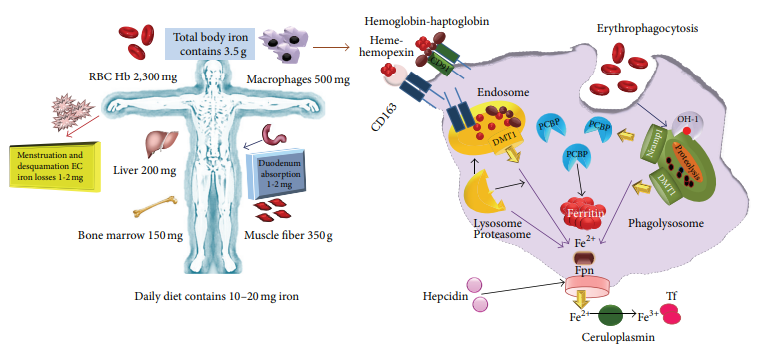
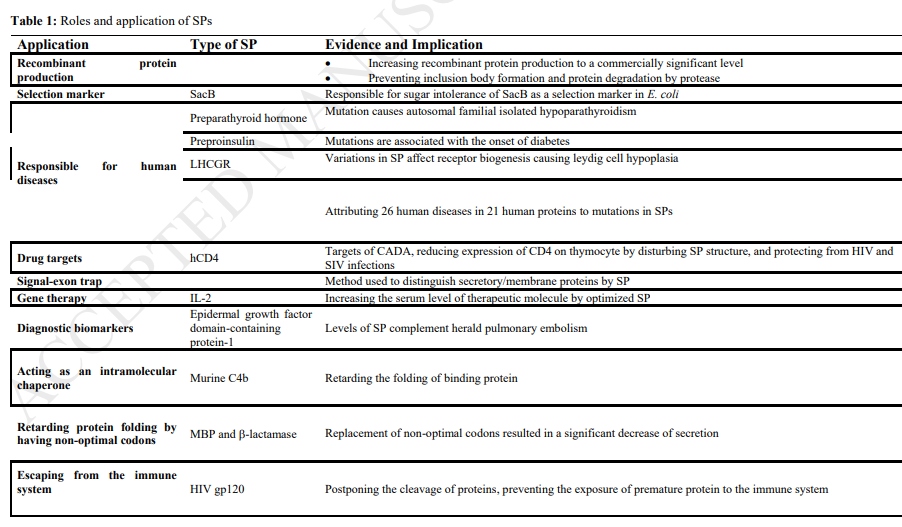
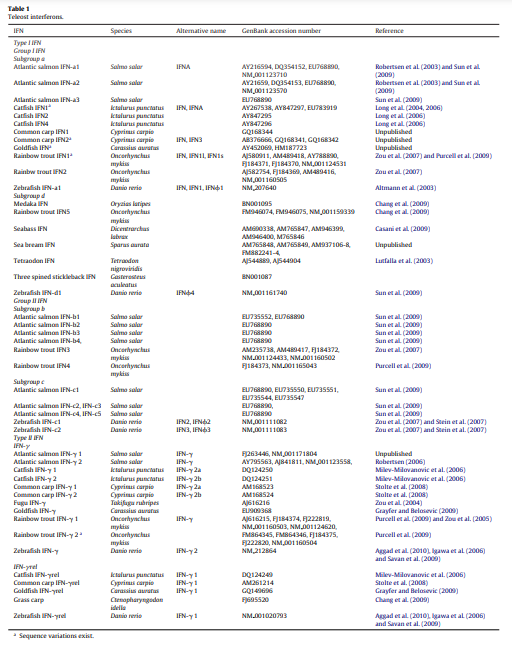
1. IntroductionInfectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites can be categorized into extracellular or intracellular pathogens from an immunopathological perspective. Most encounters with these pathogenic agents lead to an acute infection, followed by the development of clinical signs. These infections are relatively brief, and in a healthy host, following onset of appropr..