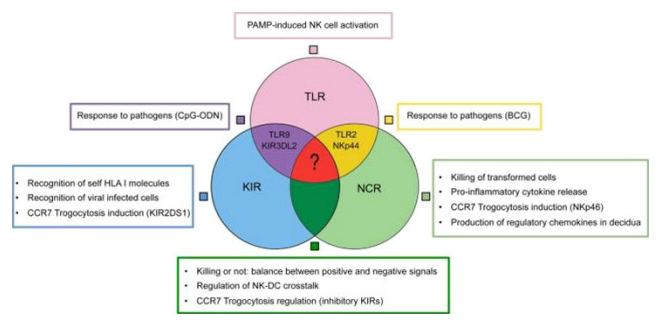
TROGOCYTOSISTrogocytosis, a form of cell-to-cell interaction widely existing in a species or between different species, involves one cell contacting and quickly “biting” another cell. This interaction was first described in 1970 as part of the process of parasites attacking and killing host cells (1). In 2002,it was given its name from the ancient Greek word “trogo”, which means “nibbling” to de..