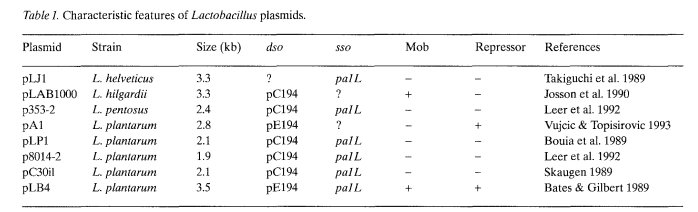
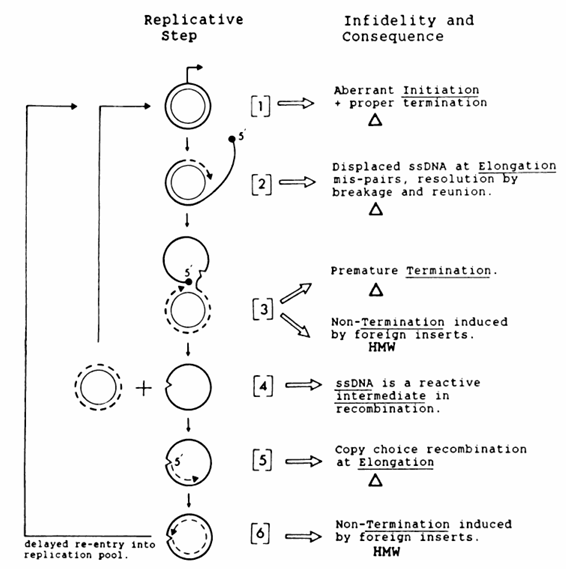
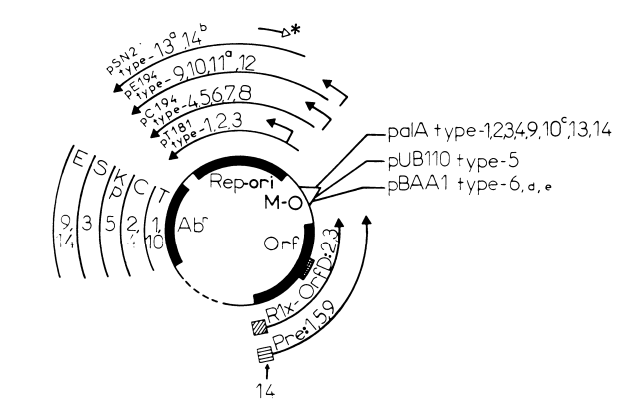
Introduction The genus Lactobacillus belongs to the family of Lactobacteriaceae also known as lactic acid bacteria, a group of microorganisms that have been used for centuries in the preparation and processing of foods and beverages (Rose 1982; Kandler 1984; Chassy 1985, Chassy 1987). These rod-shaped, anaerobic to micro-aerophilic, non-pathogenic bacteria, which produce lactic acid as their maj..